Spring's arrival brings a sense of renewal and hope. But in recent years, whispers of an earlier spring have turned into shouts. Here in 2024, the question isn't just "is spring early?" but "how much earlier, and what does it mean?"
This blog delves into the science behind spring's shift, explores how it's impacting your town (data permitting!), and offers resources to stay informed and take action.
What is Phenological Change?
Phenology is the study of naturally occurring events in plants and animals that are influenced by climate. Flowering plants, migrating birds, and insect emergence typically mark spring's arrival. Environmental cues like temperature, daylight hours, and rainfall patterns trigger these events.
However, these environmental cues are shifting due to climate change, particularly rising global temperatures. Warmer winters and earlier snowmelt create conditions that trick plants and animals into believing spring has arrived sooner.
What is the vernal equinox?
The vernal equinox, also known as the March equinox, is when the Sun crosses the celestial equator – an imaginary line above Earth's equator – from south to north. This happens around March 19th, 20th, or 21st every year.
-
Date: It occurred on Tuesday, March 19th, 2024 at 11:06 PM EDT (which is Wednesday, March 20th, 2024 at 3:06 UTC).
-
Significance: It marks the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Day and night are roughly equal in length all over the world on this day.
Signs of an Early Spring
Traditionally, spring's arrival is marked by a combination of factors: warmer temperatures, blooming flowers, and earlier bird migrations. Let's see how these indicators are shaping up in 2024:
Spring is warming up across the United States! Since 1970, the average spring temperature has increased by 2°F. This warming trend is evident across the country, with 229 cities experiencing an average increase of 2.2°F in spring temperatures. The Southwest is feeling the heat the most, with some locations in Nevada, Texas, and Arizona warming by over 6°F since 1970.
Source: 2024 Spring Package
This isn't just about the average temperature – we also see more warm days in spring. Roughly 73% of locations studied now have at least 7 more days with warmer-than-normal temperatures compared to 1970. As our world warms, spring arrives earlier, leading to longer allergy seasons, earlier snowmelt, and extended growing seasons.
Temperature: Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reveals warmer-than-average temperatures across much of the US for the first two months of 2024. The Old Farmer's Almanac spring forecast for 2024 predicts above-average temperatures in March for most areas along the East Coast, except for Florida. This warmth is accelerating plant growth.
| Statistic | Increase | Locations Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Warmer-than-normal spring days | Up to 18 days more | 96% (230 out of 239 locations) |
| Average spring temperature increase | 2.2°F | 96% (229 locations) |
| Locations with 2°F or more warming | - | 54% (129 locations) |
| Region with most warming | Southwest | 3.3°F average increase |
| Top 5 warming cities | ||
| Reno, Nevada (6.8°F) | ||
| El Paso, Texas (6.3°F) | ||
| Las Vegas, Nevada (6.2°F) | ||
| Tucson, Arizona (6°F) | ||
| Phoenix, Arizona (5.3°F) |
-
Spring across the U.S. is experiencing a significant rise in temperatures.
-
On average, spring temperatures have risen by 2.2°F since 1970.
-
The Southwest region shows the most significant warming trend, with an average increase of 3.3°F.
-
Several cities, particularly in the Southwest, have seen dramatic increases in spring temperatures (up to 6.8°F).
Plant Phenology: The National Phenology Network (NPN) tracks the timing of biological events like plant development. Their 2024 Spring Index data (as of March 14th) shows a surge of early leaf growth in the East, Midwest, and Southeast.
SPRING FIRST LEAF INDEX
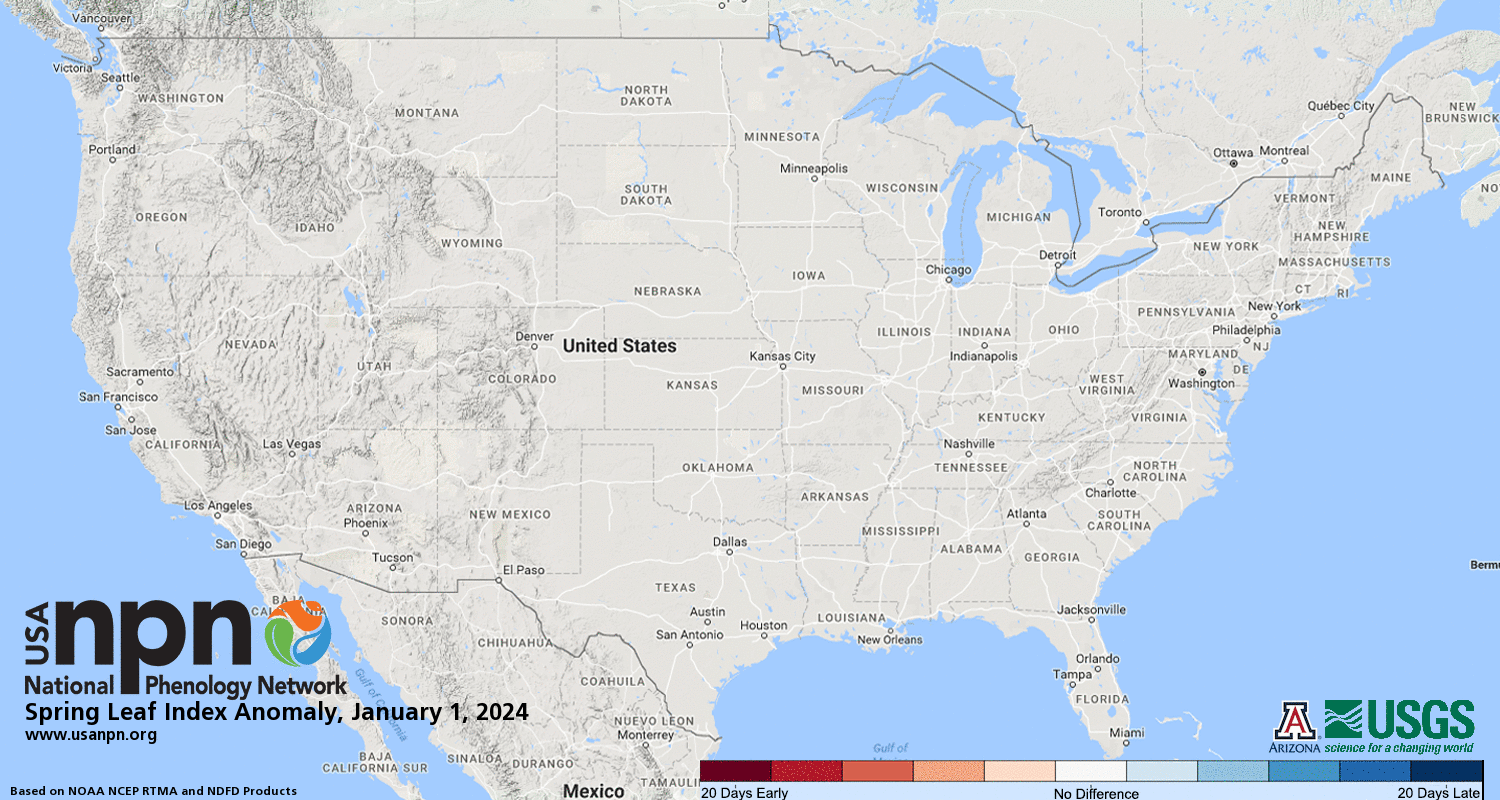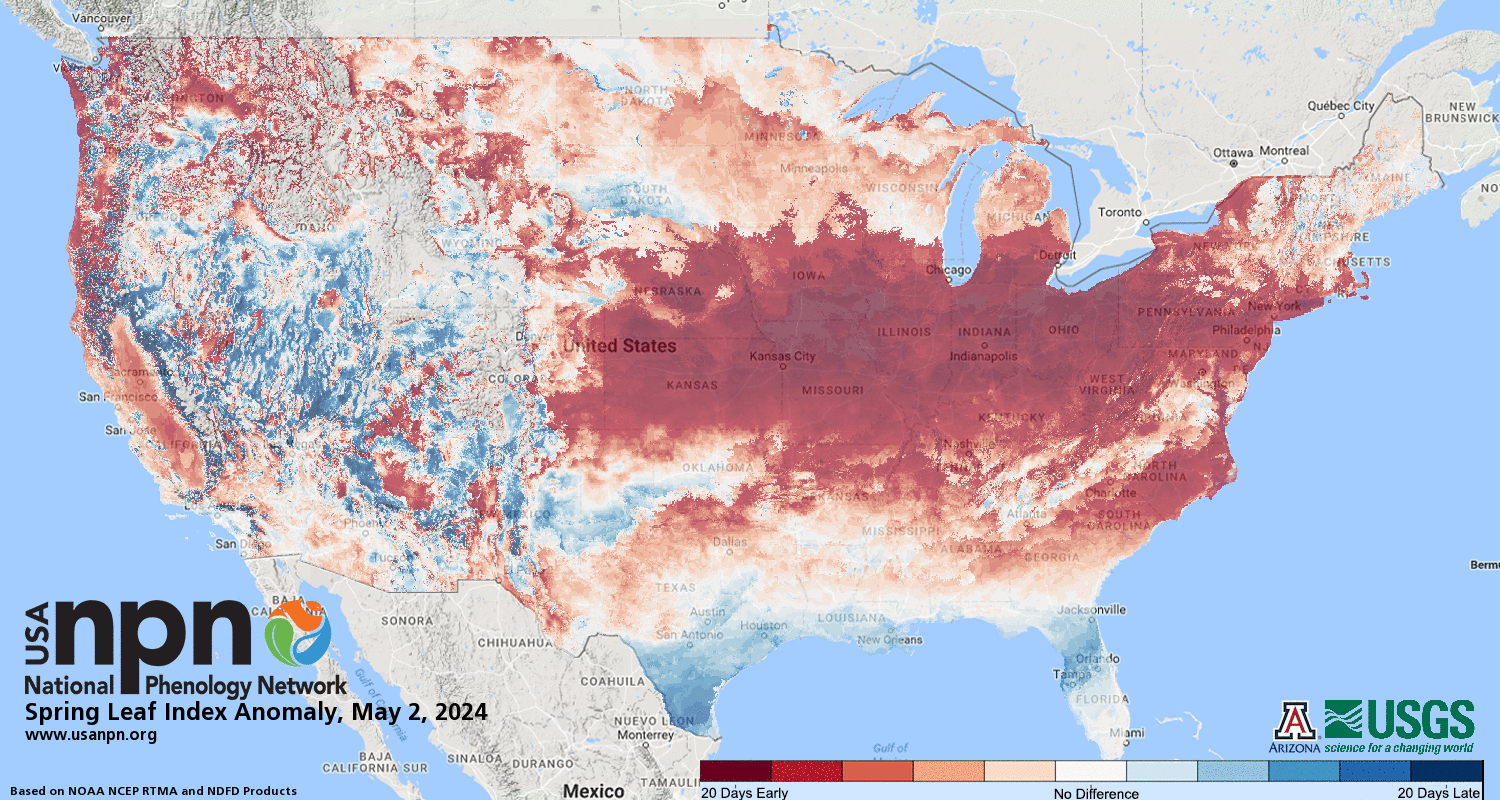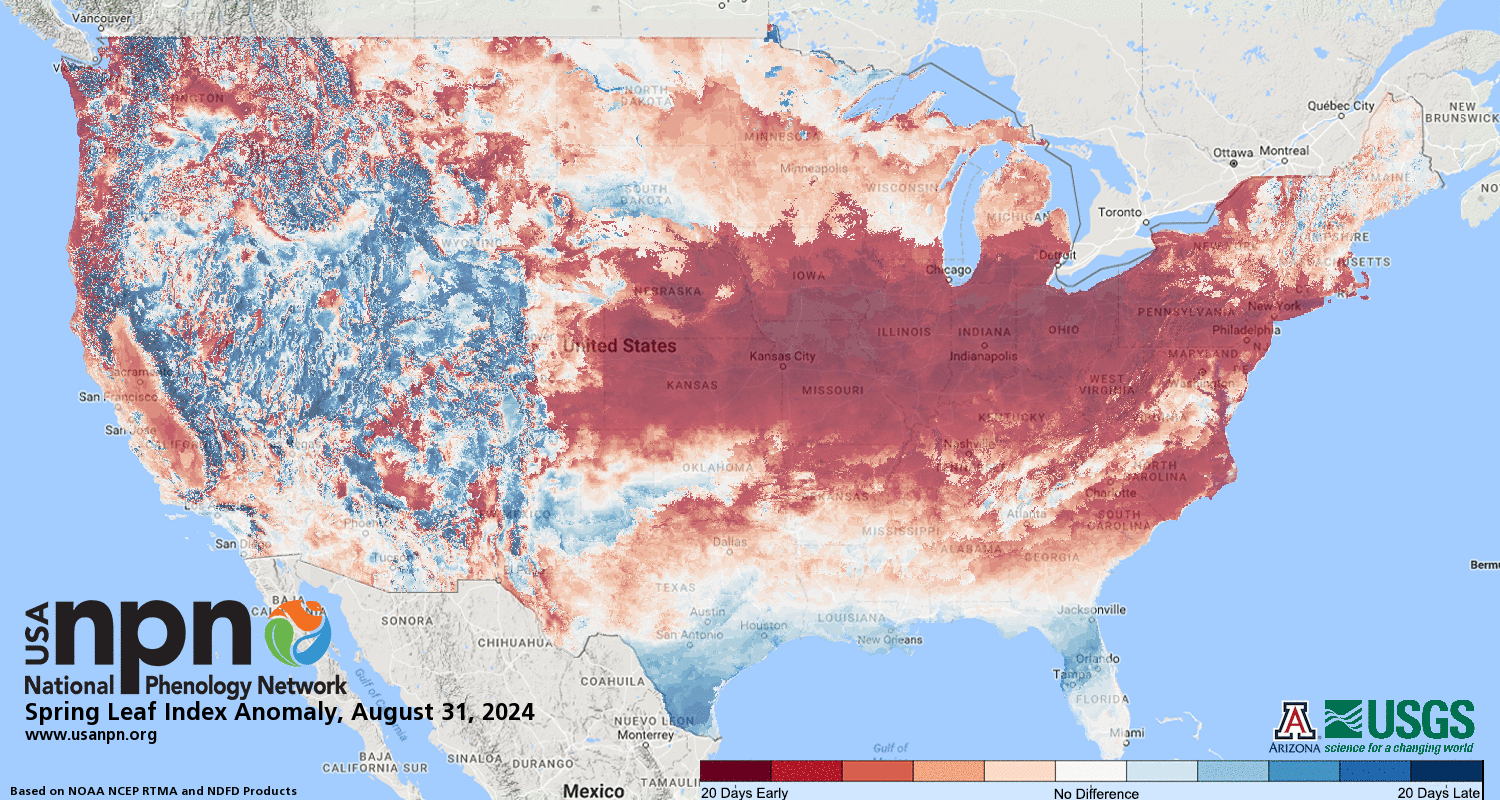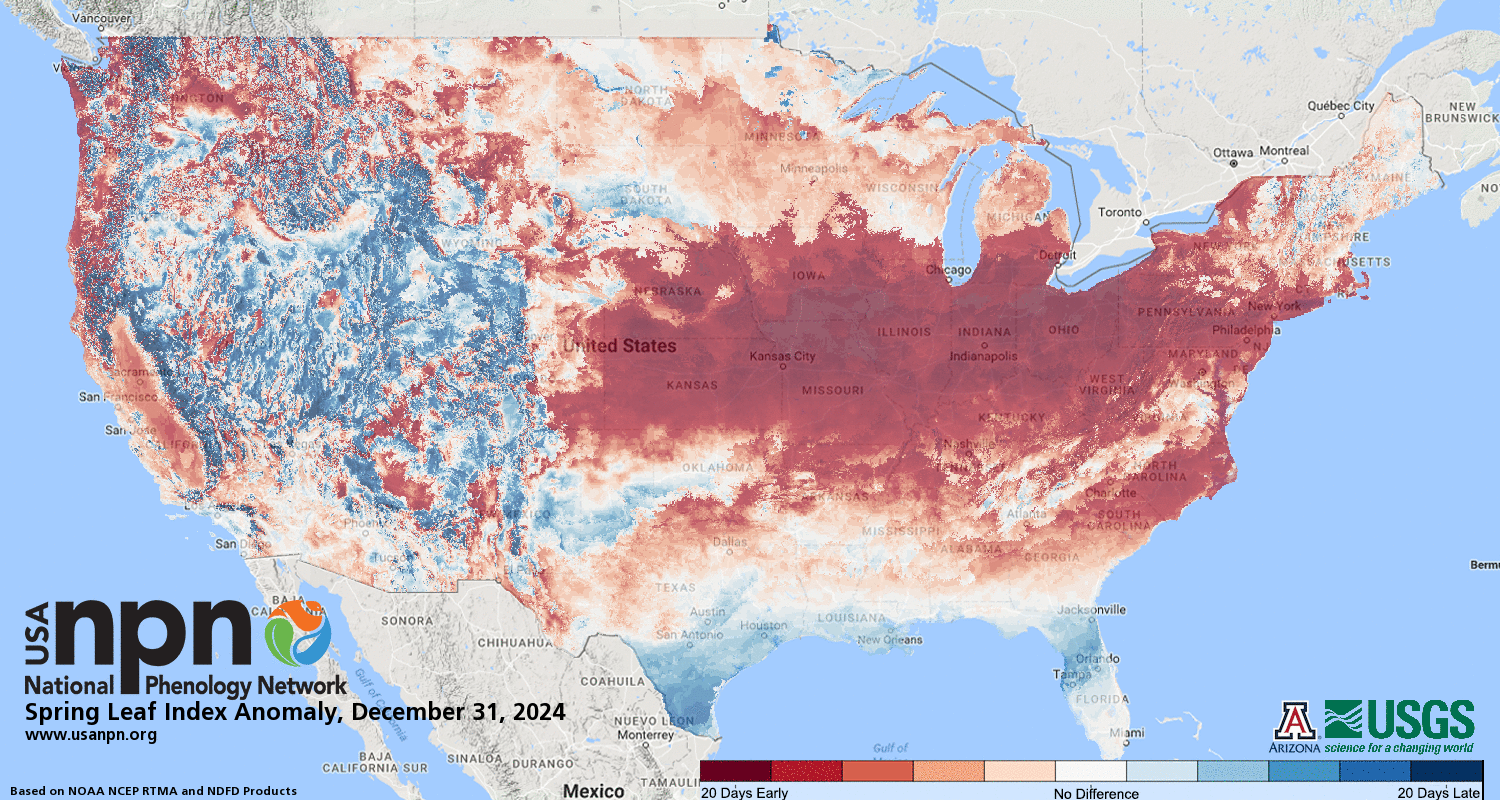
SPRING FIRST BLOOM INDEX
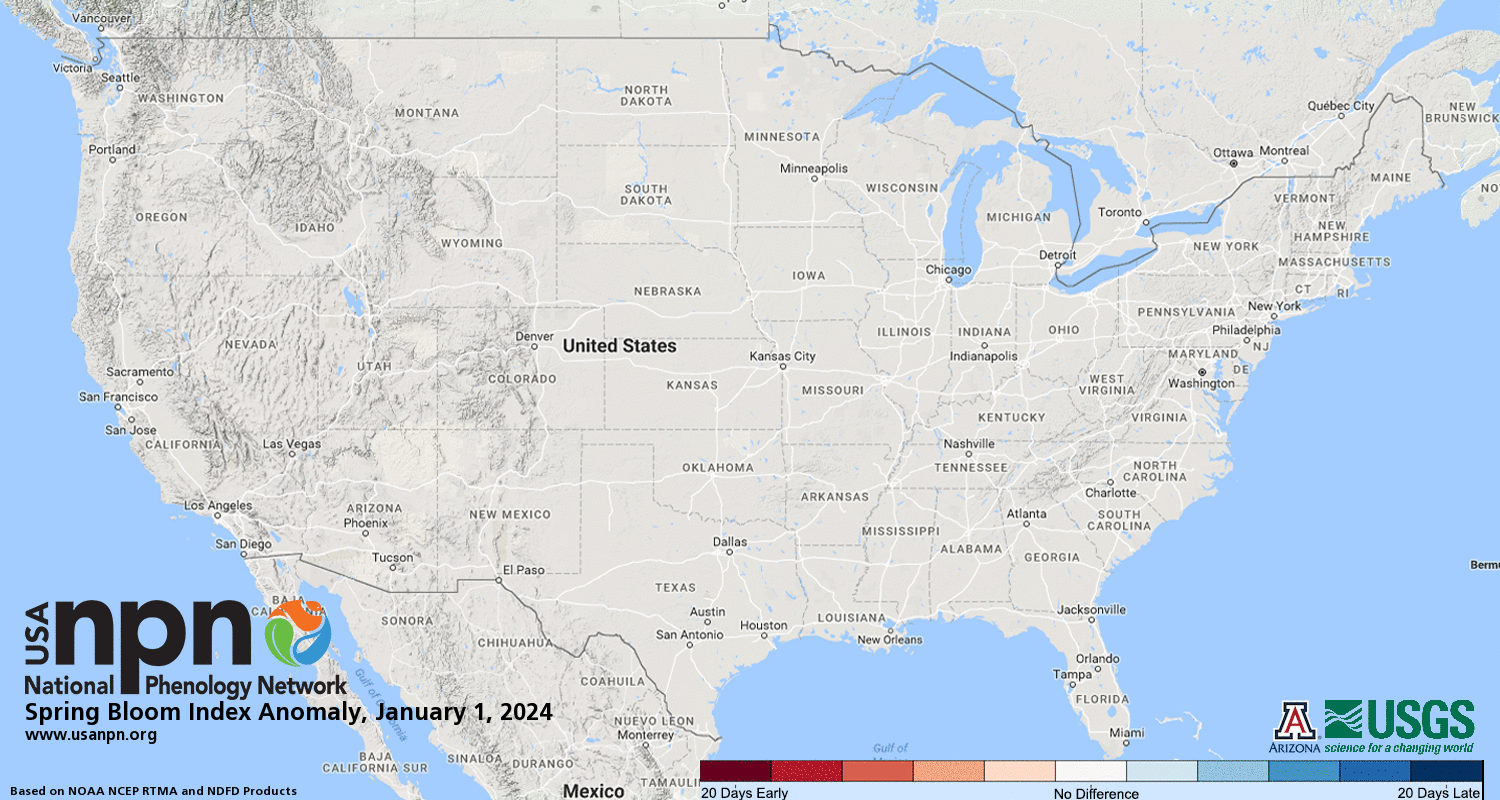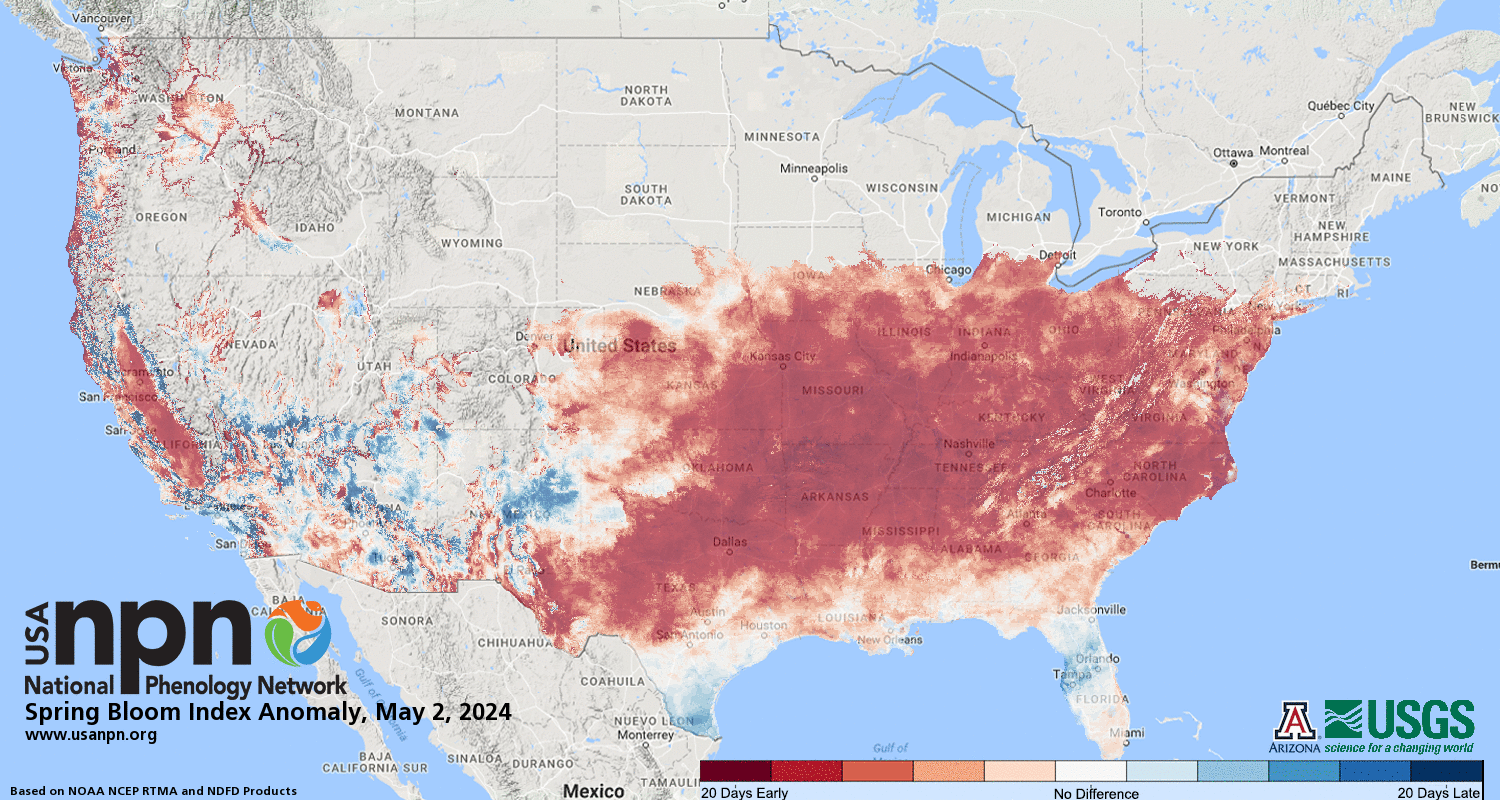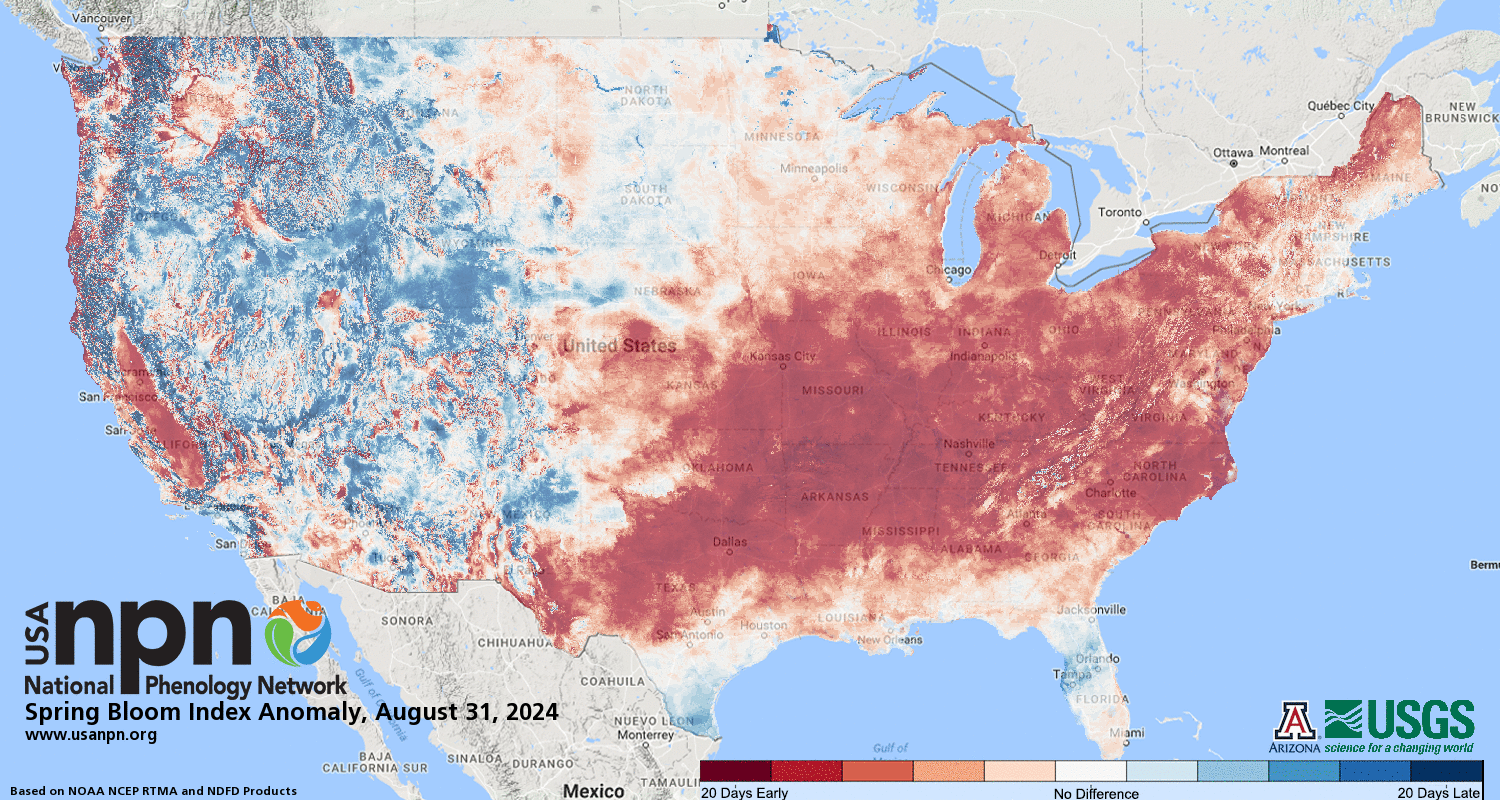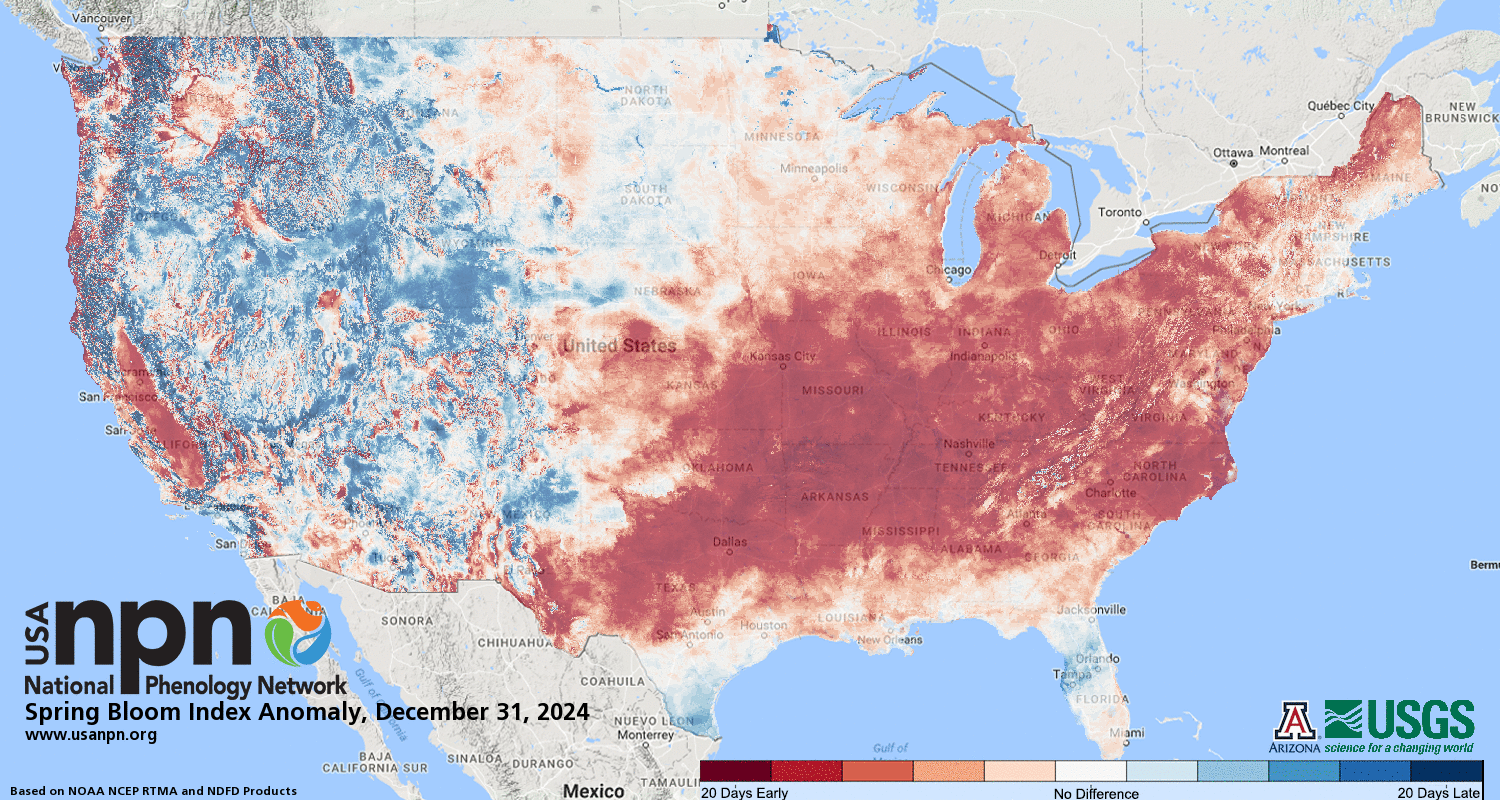
For example, Omaha, Nebraska is 20 days ahead of schedule, Indianapolis, Indiana is 14 days early, and New York City is 10 days ahead compared to the historical average (1991-2020).
Bird Migration: The National Audubon Society reports earlier bird arrivals in many regions.
For instance, some birdwatchers have documented robins returning to their nesting grounds in the Northeast a week or two earlier than usual.
Spring is indeed arriving earlier in many parts of the US in 2024, echoing a long-term trend.
Earlier Springs and Climate Change
The earlier arrival of spring isn't a one-off event. Numerous studies have documented this phenomenon over the past few decades. Here are some key findings:
Research published in Salon.com in 2020 highlights regional variations. The Northeast has seen a six-day advancement in spring arrival, while the Southwest has experienced a more dramatic shift of approximately 19 days.
These trends strongly correlate with rising global temperatures, primarily driven by human activity and greenhouse gas emissions. A warmer planet leads to earlier snowmelt, influencing soil temperatures and triggering earlier plant development.
Ecological Consequences of Early Springs
While an earlier spring may seem pleasant initially, it has significant ecological ramifications:
-
Mismatched Timing: Plants and animals rely on historical cues like temperature and day length to trigger essential life stages like migration, breeding, and food acquisition. An earlier spring disrupts these well-established cycles. For example, earlier blooming plants might leave pollinators like bees with a limited food supply if they haven't emerged yet.
-
Pest and Disease Outbreaks: Warmer temperatures can favor the survival and spread of certain insects and diseases. Earlier springs could lead to increased pest outbreaks, impacting agricultural productivity and potentially threatening native plant populations.
-
Habitat Disruption: As spring arrives earlier, some species may struggle to adapt their seasonal movements. This can disrupt delicate ecological balances and lead to habitat loss for certain species.
Here are some general emergency essentials to have on hand year-round, that may be even more critical during unpredictable spring weather:

Link to Buy: Keystone Meats
Adapting to a Changing Spring
The earlier arrival of spring is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. Here's what we can do:
-
Continued Monitoring: Continued data collection and analysis by organizations like the NPN are crucial for understanding the long-term trends and regional variations of earlier springs.
-
Conservation Efforts: Protecting and restoring natural habitats can help species adapt to changing environmental conditions. This includes creating corridors for species migration and managing invasive species.
-
Sustainable Practices: Mitigating climate change is paramount. Reducing our carbon footprint through renewable energy sources and sustainable practices will help stabilize global temperatures and create a more predictable spring season.
The Human Impact: Challenges and Opportunities
-
Agriculture: Farmers rely on predictable temperature patterns to plan planting, manage crops, and schedule harvests. Earlier springs can disrupt these established routines, potentially leading to crop failures and economic losses. Additionally, changes in pest and disease outbreaks may necessitate adjustments in pest control strategies.
-
Public Health: Warmer temperatures can increase air pollution levels, triggering allergies and respiratory problems. Earlier springs can also lead to a longer allergy season, impacting people's health and quality of life. Additionally, increased tick and mosquito populations can pose a greater risk of tick-borne and mosquito-borne illnesses.
-
Outdoor Recreation: Earlier snowmelt and warmer temperatures can extend the season for activities like hiking, fishing, and camping. However, this can also lead to increased water stress in some regions, impacting recreational activities that rely on healthy water resources.
What Can We Do?
-
Plant Native Species: Planting native flowering plants that bloom at the appropriate time can provide reliable food sources for pollinators.
-
Support Sustainable Agriculture: Choose to purchase food grown using sustainable practices that minimize pesticide use and support healthy ecosystems.
-
Conserve Water: Implement water-saving practices in your home and garden to help manage any potential water scarcity.
-
Citizen Science: Participate in citizen science projects to contribute valuable data on phenological changes.
-
Advocate for Climate Action: Support policies that address climate change and promote a transition to renewable energy sources.
By taking these steps, we can build a more resilient future for ourselves and the natural world.
Understanding the earlier arrival of spring requires a collaborative effort. By combining scientific research with citizen science initiatives and individual action, we can improve our understanding of this phenomenon and adapt our practices to minimize its ecological consequences.
What are the dates for the four seasons in 2024?
-
First day of spring: March 19, 2024
-
First day of summer: June 20, 2024
-
First day of fall: Sept. 22, 2024
-
First day of winter: Dec. 21, 2024


